
Full frame sensor size full#
Generally, a full frame sensor can provide a broader dynamic range and better low light/high ISO performance yielding a higher quality image than a crop sensor. Full Frame Advantages Dynamic Range and Wider Angles We are going to avoid the technical details and just give you the most practical and general information. There are several advantages and disadvantages to each sensor size. Advantages and Disadvantages of Full Frame and Crop Sensors

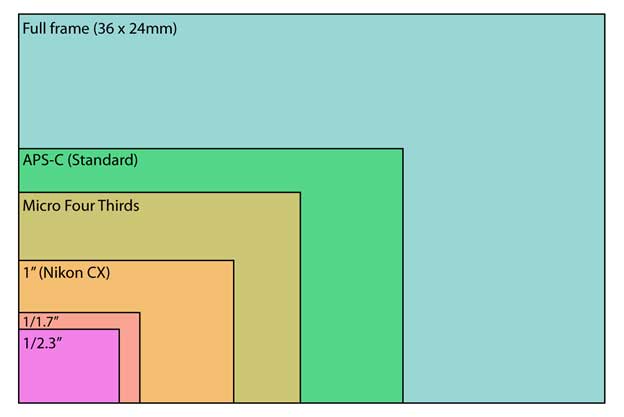
When a Nikon 50mm f/1.4 lens is attached to that Nikon DSLR, the focal length is multiplied by 1.5x and effectively acts like a 75mm lens on a full frame DSLR. The amount of difference in the field of view or focal length with a crop sensor is measured by its “Multiplier.”įor example, a Nikon APS-C crop sensor has a 1.5x multiplier. This effectively increases the focal length. If you use a crop frame camera, the sensor will crop out the edges of the frame. In other words, if a full frame DSLR and a crop sensor DSLR take the same photo from the same distance, with the same lens and point of view, then the crop sensor will capture a tighter field of view than the full frame.įocal length measurements on lenses are based on the 35mm standard. The smaller sensor’s field of view is a crop of the full frame. In fact the term “crop” implies just exactly that. The most visible difference between full frame and crop sensor is their field of view.

Crop Sensor Field of View and Focal Length The common types of crop sensor include APS-C and micro 4/3 systems. A crop sensor refers to any sensor smaller than a full frame sensor or a 35mm film frame. The differences between the full frame vs crop sensor are not limited to size, but it’s a good place to start. The Difference between Full Frame Vs Crop Sensors


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
